The Current Landscape
In Australia, the cost of natural disasters is forecasted to quadruple from $6.3 billion per year to $23 billion. The start of 2020 has seen bushfires, floods and severe hailstorms with the frequency of extreme weather events predicted to increase over the next decade.
Environmental emergencies constitute a major economic threat to Australia's economy, environment and communities. We're working with government and industry partners to better develop and enhance the nation's response to this new normal.
From localised initiatives, such as predictive analysis of floods and bushfires, through to global disaster risk mapping, we're committed to ensuring our preparedness to disasters is world leading.
Our Capabilities
Our research aims to provide unprecedented situational awareness and decision support for mitigating, responding, and recovering from environmental disasters.
This research can help emergency workers, crisis managers, decision makers and other personnel better prepare strategic, tactical and real-time planning and post-recovery efforts.
Our capabilities include:
- Data visualisation
- Advanced data mapping
- Mass data integration
- Predictive analytics
- Monitoring, surveillance and sampling design strategies
- Spatio-temporal modelling, prediction and forecasting
- Quantitative risk assessment approaches across the broader environmental and agricultural sectors
Our Work
Spark

An open framework for fire prediction and analysis, Spark takes our current knowledge of fire behaviour and combines it with state-of-the-art simulation science to produce predictions, statistics and visualisations of bushfire spread.
Spark can read meteorological data and use wind, temperature and humidity information directly within its models. Geographic information such as land slope, vegetation, and un-burnable areas such as roads and water bodies can also be incorporated, each with their own defined fire spread rate.
The platform also allows simulation of any number of distinct fire fronts, multi-front interaction, and coalescence as the fire evolves.
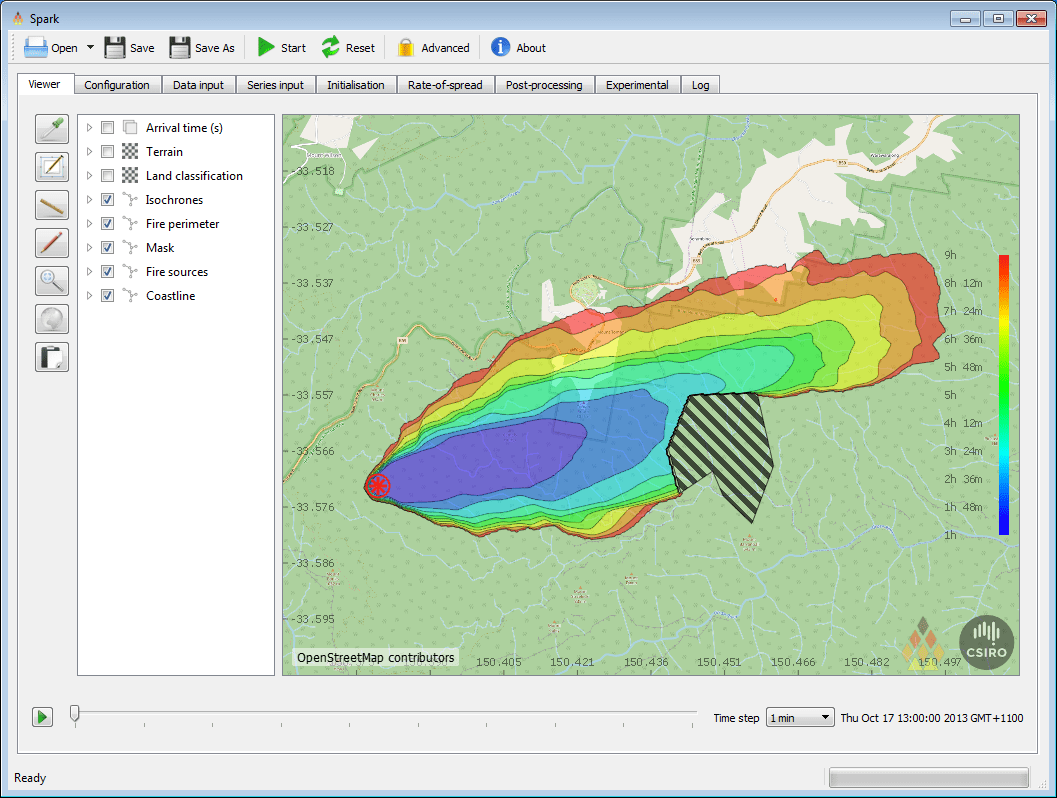
Spark - A wildfire simulation toolkit
Swift
Swift (Shallow Water Integrated Flood Tool) is a toolkit for the end-to-end processing, simulation and analysis of floods.

It employs computational fluid dynamics to develop a high-resolution 3D flood modelling technique that delivers realistic water simulations, including difficult-to-model behaviours such as wave motions, flow of solids, wave fragmentation and splashing.
Swift incorporates information about urban infrastructure and conditions - such as canals and weather forecast data -- to provide a visual representation of what may happen if flooding occurs. Swift's capabilities have been applied to numerous flood mitigation projects for cities across Australia.
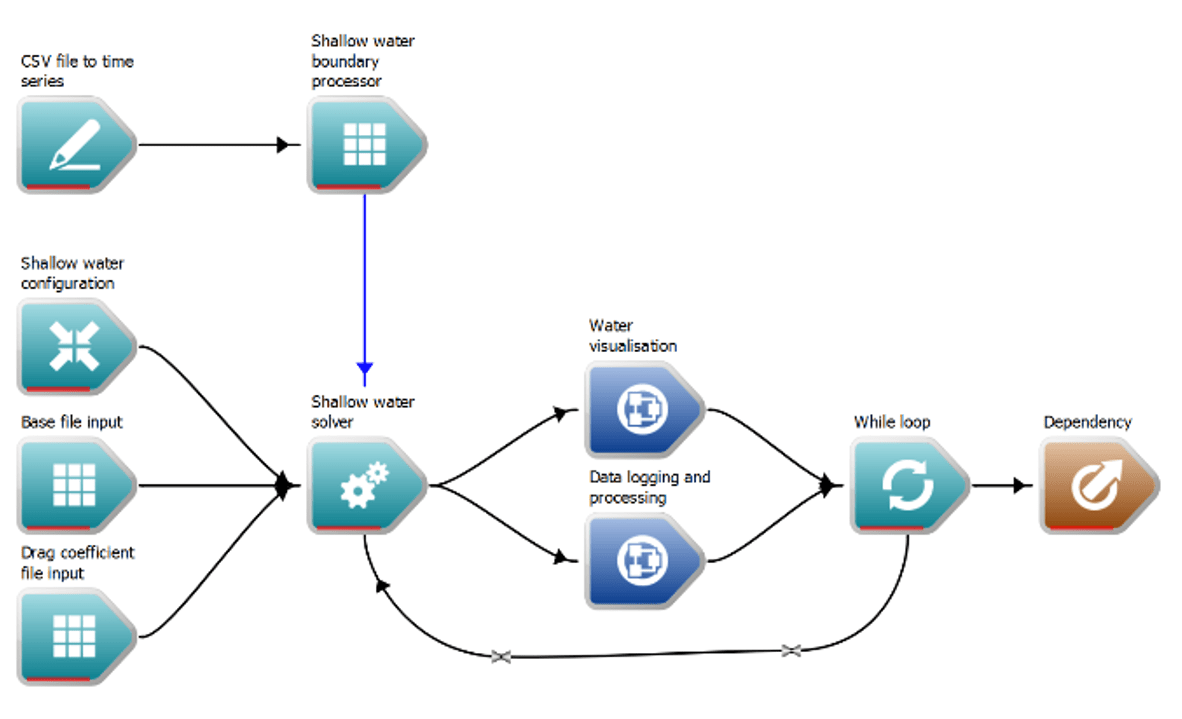
Swift - A shallow water based integrated flood toolkit
NSW Spatial Digital Twin
Digital Twins create virtual replicas of small and large-scale physical objects, buildings, cities, regions and systems, a technology game-changer for the future of smart cities.
The NSW Spatial Digital Twin has been selected to securely house, organise, and visualise the data needed to develop effective management strategies for disaster planning, preparedness, response and recovery.
The integration of a 3D spatial dataset mapping the locations of telecommunication towers and assets across NSW into the Digital Twin will enable emergency service organisations to better understand and protect these vital locations before and during an environmental event. The Twin was identified by The NSW Independent Bushfire Enquiry to inform emergency responders as to what telecommunications services are and aren’t accessible for operational use, what services are available to the community, and ensure residents have the greatest possible prospect of retaining communications and connectivity during a crisis.
The Twin is also being used to map and compare environmental data, providing crucial insights to better prepare and inform areas and communities in the future. Below, the NSW Spatial Digital Twin compares the town of Windsor located in the Hawkesbury region pre and post-the March 2021 NSW floods.
ESA
Our Emergency Situation Awareness (ESA) platform is a social media, all-hazard analysis platform that monitors public user content on Twitter across Australia and New Zealand in real-time, converting a massive amount of data into situation awareness information for crisis coordinators.
It can generate alarms for unanticipated incidents like earthquakes or fast-moving events like bushfires. Information detected via the ESA could contribute to an improved understanding of the scope and impact of events such as earthquakes, cyclones, bushfires and floods.
ESA can also enable evacuation planning, providing precious extra time to the emergency management workers on the ground.
Emergency Situation Awareness - Social Media Analysis for All-Hazards.
Drought Map
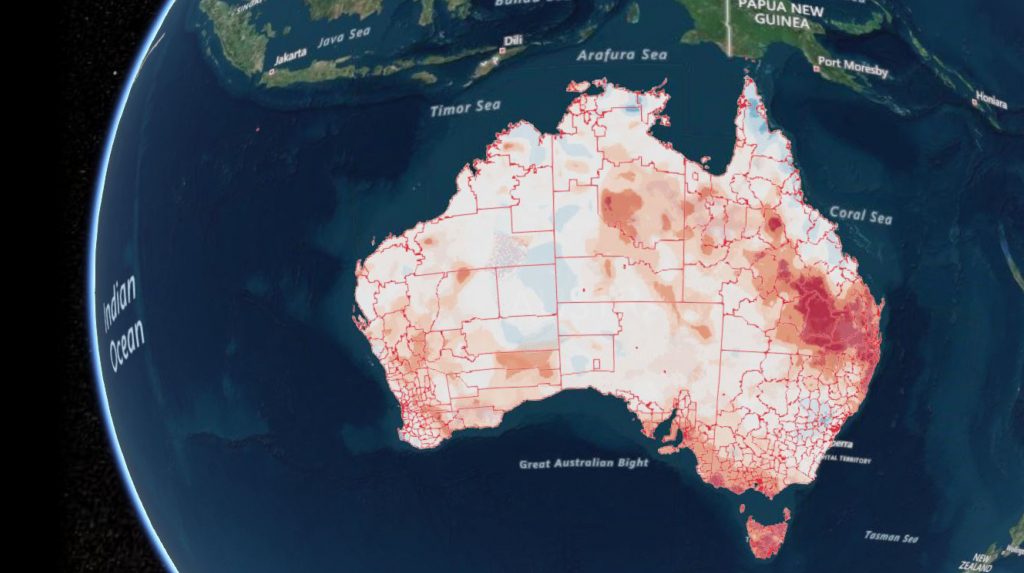
In collaboration with the Joint Agency Drought Task Force, CSIRO's Data61 has applied its award-winning advanced mapping software, TerriaJSTM, to help governments and other stakeholders combat drought.
The technology offers deep insights into current drought conditions to determine whether to deploy more support. It also facilitates coordination of response and provides information on the spread of drought using the latest meteorological information.
Tackling Drought with Data Visualisation
Indra
In a world with emerging uncertainty around environmental and climatic risk, the need to translate risks into impacts and adaptation opportunities at infrastructure scale is paramount. There are challenges when it comes to comprehensively understanding the impacts of climate change on the sustainability of a business.
At CSIRO's Data61, we see the primary challenges being accessibility to data, the interoperability of datasets and platforms, and the insights derived from big data. Through technologies and capabilities across CSIRO, we take a holistic approach to addressing climate risk. In this context, working closely with CSIRO Oceans & Atmospheres, we have developed INDRA; a platform technology which encompasses climate change, hazard and vulnerability related inputs from various areas of CSIRO, along with key data inputs from relevant agencies such as the Bureau of Meteorology and state and city based planning departments.
Indra is a geospatially enabled big data analytics platform that allows the integration of a range of relevant datasets, including climate, natural hazards, infrastructure, demographics and economic metrics to provide data driven critical insights. It is cloud enabled and can be accessed via any of the leading cloud providers, and hosted on the web for ease of use and interoperability with other relevant tools. Indra has been used by cities and utilities to understand their infrastructure risk, and to plan for future adaptation, mitigation and financial de-risking strategies.
The key challenges and INDRA advantages include:
- Accessibility to and transparency of data
- Interoperability of data
- Magnitude of data and relevated insights
- Customisable complex analytics
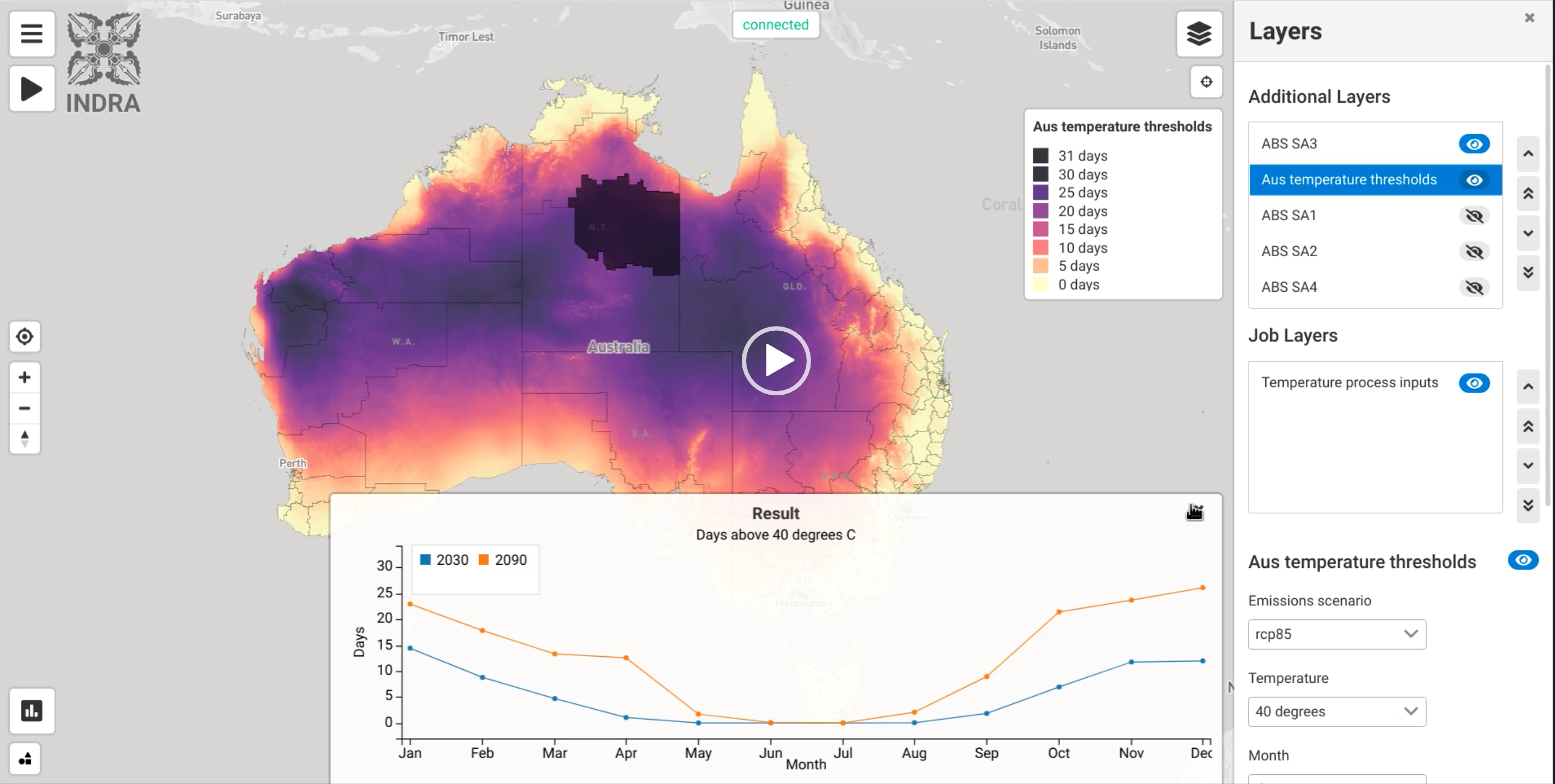
Indra has a strong history of development with applications related to bushfires, floods (catchment and coastal), erosion and groundwater risks across all levels of government, multiple agencies and corporate partners. As a result, the team at CSIRO have access to a range of related relevant datasets through partnerships with the BoM, state based environmental and land agencies such as DELWP and Infrastructure NSW, and from Universities, where relevant.
By visualising and analysing these datasets in a common, federated platform, the end user will be able to better understand the data landscape, and have transparency into the modelling and analytic process.
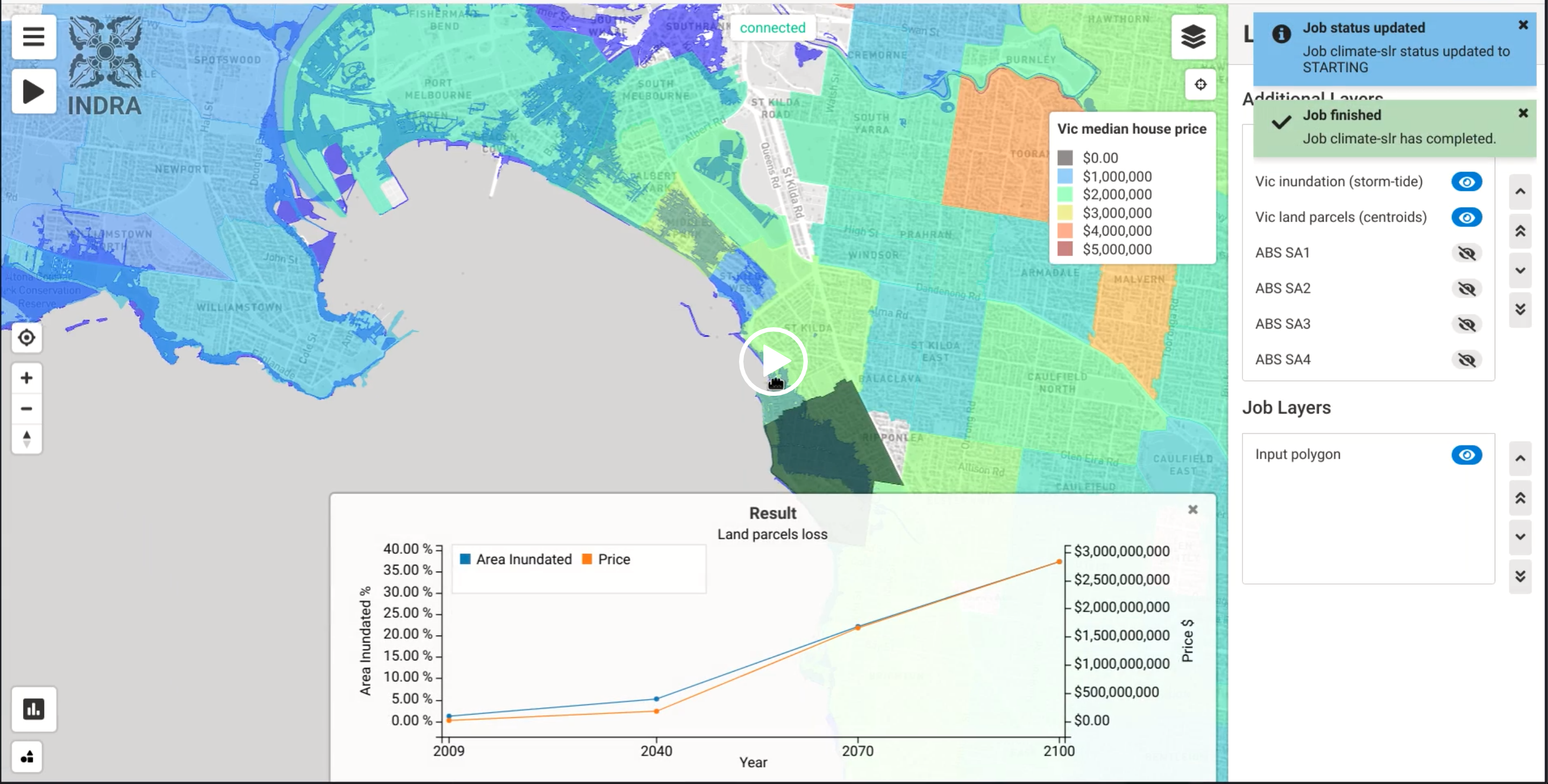
INDRA is best thought of as a "product builder" with a focus on climate related challenges. Use cases for INDRA include:
- INDRA for Coastal Urban Infrastructure Risk Applications
- INDRA for Rural/Agricultural Applications focussing on climate risk from a crop yield perpective.
- INDRA for Cities and Utilities related Risk Applications.
- INDRA for the Globe using a range of Global Climate Modelling Projections.
The INDRA analytics and visualisation platform can be used to develop custom integrated products for the client which is easily accessible on the web, and hosted on the cloud, scaleable both in terms of geography, and international applications. We are currently trialling applications of INDRA in the Pacific Island nations and in Victoria and Tasmania with the intention to scale to other global destinations.
Climate and Hazard Risk Analytics Engine - INDRA
CSIRO links to INDRA
- Downscaled Climate Change Related Datasets - Developed by CSIRO Oceans & Atmospheres
- Downstream Hazard Modelling Capabilities - In development by CSIRO's Data61
The Current Landscape
In Australia, the cost of natural disasters is forecasted to quadruple from $6.3 billion per year to $23 billion. The start of 2020 has seen bushfires, floods and severe hailstorms with the frequency of extreme weather events predicted to increase over the next decade.
Environmental emergencies constitute a major economic threat to Australia's economy, environment and communities. We're working with government and industry partners to better develop and enhance the nation's response to this new normal.
From localised initiatives, such as predictive analysis of floods and bushfires, through to global disaster risk mapping, we're committed to ensuring our preparedness to disasters is world leading.
Our Capabilities
Our research aims to provide unprecedented situational awareness and decision support for mitigating, responding, and recovering from environmental disasters.
This research can help emergency workers, crisis managers, decision makers and other personnel better prepare strategic, tactical and real-time planning and post-recovery efforts.
Our capabilities include:
- Data visualisation
- Advanced data mapping
- Mass data integration
- Predictive analytics
- Monitoring, surveillance and sampling design strategies
- Spatio-temporal modelling, prediction and forecasting
- Quantitative risk assessment approaches across the broader environmental and agricultural sectors
Our Work
Spark

An open framework for fire prediction and analysis, Spark takes our current knowledge of fire behaviour and combines it with state-of-the-art simulation science to produce predictions, statistics and visualisations of bushfire spread.
Spark can read meteorological data and use wind, temperature and humidity information directly within its models. Geographic information such as land slope, vegetation, and un-burnable areas such as roads and water bodies can also be incorporated, each with their own defined fire spread rate.
The platform also allows simulation of any number of distinct fire fronts, multi-front interaction, and coalescence as the fire evolves.
Spark - A wildfire simulation toolkit
Swift
Swift (Shallow Water Integrated Flood Tool) is a toolkit for the end-to-end processing, simulation and analysis of floods.
It employs computational fluid dynamics to develop a high-resolution 3D flood modelling technique that delivers realistic water simulations, including difficult-to-model behaviours such as wave motions, flow of solids, wave fragmentation and splashing.
Swift incorporates information about urban infrastructure and conditions - such as canals and weather forecast data -- to provide a visual representation of what may happen if flooding occurs. Swift's capabilities have been applied to numerous flood mitigation projects for cities across Australia.
Swift - A shallow water based integrated flood toolkit
NSW Spatial Digital Twin
Digital Twins create virtual replicas of small and large-scale physical objects, buildings, cities, regions and systems, a technology game-changer for the future of smart cities.
The NSW Spatial Digital Twin has been selected to securely house, organise, and visualise the data needed to develop effective management strategies for disaster planning, preparedness, response and recovery.
The integration of a 3D spatial dataset mapping the locations of telecommunication towers and assets across NSW into the Digital Twin will enable emergency service organisations to better understand and protect these vital locations before and during an environmental event. The Twin was identified by The NSW Independent Bushfire Enquiry to inform emergency responders as to what telecommunications services are and aren’t accessible for operational use, what services are available to the community, and ensure residents have the greatest possible prospect of retaining communications and connectivity during a crisis.
The Twin is also being used to map and compare environmental data, providing crucial insights to better prepare and inform areas and communities in the future. Below, the NSW Spatial Digital Twin compares the town of Windsor located in the Hawkesbury region pre and post-the March 2021 NSW floods.
ESA
Our Emergency Situation Awareness (ESA) platform is a social media, all-hazard analysis platform that monitors public user content on Twitter across Australia and New Zealand in real-time, converting a massive amount of data into situation awareness information for crisis coordinators.
It can generate alarms for unanticipated incidents like earthquakes or fast-moving events like bushfires. Information detected via the ESA could contribute to an improved understanding of the scope and impact of events such as earthquakes, cyclones, bushfires and floods.
ESA can also enable evacuation planning, providing precious extra time to the emergency management workers on the ground.
Emergency Situation Awareness - Social Media Analysis for All-Hazards.
Drought Map
In collaboration with the Joint Agency Drought Task Force, CSIRO's Data61 has applied its award-winning advanced mapping software, TerriaJSTM, to help governments and other stakeholders combat drought.
The technology offers deep insights into current drought conditions to determine whether to deploy more support. It also facilitates coordination of response and provides information on the spread of drought using the latest meteorological information.
Tackling Drought with Data Visualisation
Indra
In a world with emerging uncertainty around environmental and climatic risk, the need to translate risks into impacts and adaptation opportunities at infrastructure scale is paramount. There are challenges when it comes to comprehensively understanding the impacts of climate change on the sustainability of a business.
At CSIRO's Data61, we see the primary challenges being accessibility to data, the interoperability of datasets and platforms, and the insights derived from big data. Through technologies and capabilities across CSIRO, we take a holistic approach to addressing climate risk. In this context, working closely with CSIRO Oceans & Atmospheres, we have developed INDRA; a platform technology which encompasses climate change, hazard and vulnerability related inputs from various areas of CSIRO, along with key data inputs from relevant agencies such as the Bureau of Meteorology and state and city based planning departments.
Indra is a geospatially enabled big data analytics platform that allows the integration of a range of relevant datasets, including climate, natural hazards, infrastructure, demographics and economic metrics to provide data driven critical insights. It is cloud enabled and can be accessed via any of the leading cloud providers, and hosted on the web for ease of use and interoperability with other relevant tools. Indra has been used by cities and utilities to understand their infrastructure risk, and to plan for future adaptation, mitigation and financial de-risking strategies.
The key challenges and INDRA advantages include:
- Accessibility to and transparency of data
- Interoperability of data
- Magnitude of data and relevated insights
- Customisable complex analytics
Indra has a strong history of development with applications related to bushfires, floods (catchment and coastal), erosion and groundwater risks across all levels of government, multiple agencies and corporate partners. As a result, the team at CSIRO have access to a range of related relevant datasets through partnerships with the BoM, state based environmental and land agencies such as DELWP and Infrastructure NSW, and from Universities, where relevant.
By visualising and analysing these datasets in a common, federated platform, the end user will be able to better understand the data landscape, and have transparency into the modelling and analytic process.
INDRA is best thought of as a "product builder" with a focus on climate related challenges. Use cases for INDRA include:
- INDRA for Coastal Urban Infrastructure Risk Applications
- INDRA for Rural/Agricultural Applications focussing on climate risk from a crop yield perpective.
- INDRA for Cities and Utilities related Risk Applications.
- INDRA for the Globe using a range of Global Climate Modelling Projections.
The INDRA analytics and visualisation platform can be used to develop custom integrated products for the client which is easily accessible on the web, and hosted on the cloud, scaleable both in terms of geography, and international applications. We are currently trialling applications of INDRA in the Pacific Island nations and in Victoria and Tasmania with the intention to scale to other global destinations.
Climate and Hazard Risk Analytics Engine - INDRA
CSIRO links to INDRA
- Downscaled Climate Change Related Datasets - Developed by CSIRO Oceans & Atmospheres
- Downstream Hazard Modelling Capabilities - In development by CSIRO's Data61
